Спираль исследования
(→Termites cycle with Logs) |
(→Termites cycle) |
||
| Строка 153: | Строка 153: | ||
</graphviz> | </graphviz> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Letopisi.org cicle === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <graphviz> | ||
| + | digraph W5 { | ||
| + | layout = "neato"; | ||
| + | node [ | ||
| + | //fontsize="10", fontcolor="blue", | ||
| + | nodesep=2, shape="none", style=""] ; | ||
| + | edge [arrowhead=normal, arrowsize=0.4 len=2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ]; | ||
| + | Read -> Create -> Edit -> Connect -> Share -> Read | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | </graphviz> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
[[Категория:Деятельность]] | [[Категория:Деятельность]] | ||
Версия 15:52, 19 июля 2016
В IBL - Inquiry-based learning Most versions of inquiry learning see a continuing cycle or spiral of inquiry.
Дьюи сформулировал и обосновал мысль о тождестве акта мышления и процесса обучения и предложил онтологический алгоритм процесса мышления, в котором проявляются пять отдельных логических ступеней: (I) чувство затруднения, (II) его определение и определение его границ, (III) представление о возможном решении, (IV) развитие путем рассуждения об отношениях представления, (V) дальнейшие наблюдения, приводящие к признанию или отклонению, т.е. заключение уверенности или неуверенности.
Заданное работами Дьюи отношение к акту мышления и обучения, как к постоянному развитию и преодолению затруднений, получило дальнейшее развитие в работах других исследователей. Дж. Брунер рассматривал исследовательскую деятельность, в ходе которой ученик овладевает новыми знаниями, как цикл развития, в котором ученик переходит от постановки вопроса к исследованию, созданию, обсуждению, обдумыванию и постановке новых вопросов «Исследуй > Создавай > Обсуждай > Обдумывай > Спрашивай >» [Брунер, 1977; Брунер, 2006].
Сходную позицию занимает Д. Колб в своей концепции экспериментального обучения [Kolb, 1984].

Содержание |
IBL Spiral

Ask -> Investigate -> Create -> Discuss -> Reflect -> Ask
Globaloria Spiral
Participate: Use the Globaloria Social Learning Network to work in teams, learn to solve programming problems and share computational knowledge publicly. Learn to collaborate onsite with classmates and educators, as well as virtually with students in other schools, and professional game makers and programmers.
Publish: Learn how to present and publish designs, code, and games online.
Play: Play to discover what makes a great educational game. Learn about game mechanics, simulations, genres, and design principles. Get inspired!
Program: Write the code for your game in Flash ActionScript. Learn to program, test, and get help from experts using tutorials and virtual network for communication.
Plan: Decide who the audience is and what your game is going to do. Research learning topics and learn your game content. Organize your ideas in a written plan. Keep adding to the plan as your research and design develops.
Prototype: Draw and videotape your game concept and test your prototype with users. Learn to use Flash to create an interactive demo that shows how the game will look.
Play -> Plan -> Prototype -> Program -> Publish -> Play

Scratch spiral
imagine what they want to do, create a project based on their ideas, play with their creations, share their ideas and creations with others, reflect on their experiences
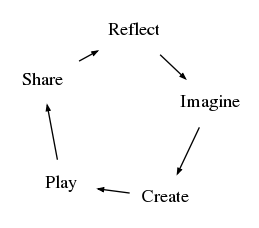
Termites cycle
см. Муравейник
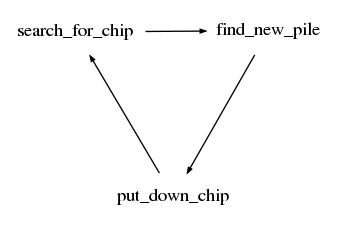
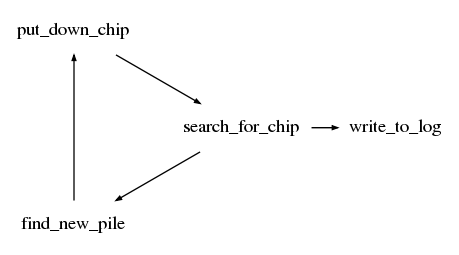
search-for-chip find-new-pile put-down-chip
Termites cycle with Logs
Letopisi.org cicle

